In the realm of political ideologies, conservatism and progressivism represent two distinct visions for society, governance, and the role of government. These ideologies often clash on fundamental issues, reflecting contrasting perspectives on social, economic, and cultural matters. Let’s delve deeper into the core principles and differences between conservatism and progressivism to gain a better understanding of these competing ideologies.
Defining Conservatism: Tradition and Stability
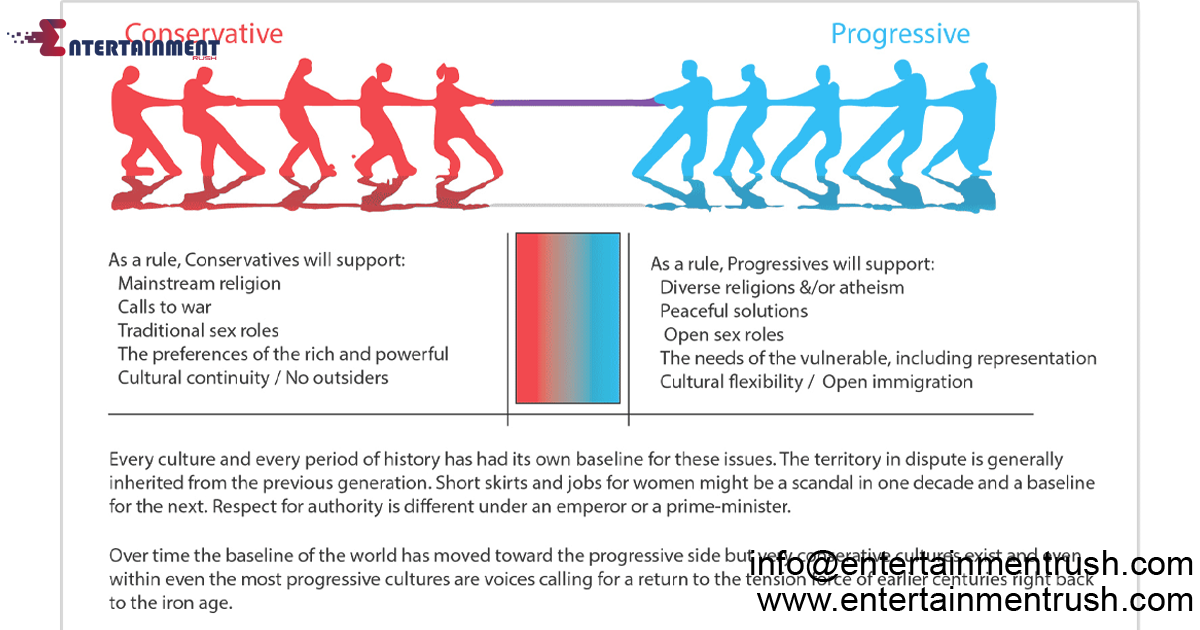
Conservatism emphasizes traditional values, institutions, and practices. It advocates for preserving established social norms, cultural traditions, and hierarchies. Central tenets of conservatism include respect for authority, individual responsibility, and skepticism toward rapid societal change. Conservatives often prioritize stability, order, and continuity in governance and society.
The Pillars of Progressivism: Change and Social Justice
Progressivism, on the other hand, is characterized by a commitment to social progress, equality, and reform. Progressives advocate for addressing social injustices, promoting inclusivity, and advancing civil rights. Key principles of progressivism include embracing change, challenging entrenched power structures, and pursuing policies aimed at expanding opportunities and reducing disparities.
Views on Government and Individual Liberty
One fundamental difference between conservatism and progressivism lies in their views on the role of government and individual liberty. Conservatives generally favor limited government intervention in the economy and society, emphasizing individual freedom, personal responsibility, and free-market principles. In contrast, progressives advocate for a more active role for government in addressing social and economic inequalities, providing social safety nets, and regulating industries to protect consumers and workers.
Social Issues: Tradition versus Social Change
Conservatism tends to uphold traditional social values and norms, often opposing rapid social change or reforms that challenge established traditions. Conservatives often prioritize preserving traditional family structures, religious institutions, and cultural practices. Progressivism, on the other hand, seeks to challenge and reform social norms that perpetuate discrimination, inequality, and exclusion. Progressives advocate for LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, racial equality, and other social justice causes.
Economic Policies: Free Markets versus Regulation
In economic matters, conservatism generally favors free-market principles, limited government regulation, and lower taxes. Conservatives believe that economic prosperity and innovation thrive in a competitive, less regulated market environment. Progressives, on the contrary, support government intervention to address income inequality, ensure workers’ rights, and promote economic justice. Progressivism often advocates for progressive taxation, robust social welfare programs, and regulations to protect consumers and workers.
Environmental Stewardship and Climate Change
Conservatism and progressivism also diverge on environmental issues, particularly concerning climate change. Conservatives may be more skeptical of the urgency of climate action and advocate for market-based solutions to environmental challenges. Progressives, on the other hand, prioritize aggressive climate policies, renewable energy initiatives, and environmental regulations to combat climate change and protect natural resources.
Bridging Ideological Divides
the ideological clash between conservatism and progressivism reflects deep-seated differences in values, priorities, and visions for society. While conservatives emphasize tradition, stability, and individual liberty, progressives prioritize social justice, inclusivity, and government intervention to address societal challenges. Bridging these ideological divides requires open dialogue, mutual respect, and a willingness to find common ground while recognizing and embracing diversity of thought. Ultimately, understanding the fundamental differences between conservatism and progressivism is essential for informed civic discourse and policymaking, enabling societies to navigate complex issues and strive for a more equitable and prosperous future.



Leave feedback about this